Doctors warn of symptoms that cause oral cancer
Oral cancer is a malignant lesion appearing in the oral cavity including: tongue, mandibular gums, buccal mucosa, floor of mouth, maxillary gums, palate and lips. In which, tongue cancer is the most common, accounting for about 40%.
Currently, many risk factors related to oral cancer have been published: tobacco, alcohol, mechanical stimulation (tooth with sharp edges, poor quality dentures…), chemical stimulation ( spicy substances, foods with high salt content…), mucosal damage due to infections (periodontitis, maxillary sinusitis), viral infections (hepatitis viruses, HPV…), age. Of these factors, tobacco and alcohol are the two most commonly associated with oral cancer.
Oral cancer is a global health problem with an increasing incidence and mortality rate and is one of the 10 most common cancers. Specifically, according to GLOBOCAN 2018, each year there are about 354,000 new cases and 177,000 deaths from oral cancer.
The disease has a high mortality rate because approximately 53% of oral cancer patients present with locally advanced or distant metastases at the time of diagnosis.
Oral cancer is common between the ages of 50 and 70, with a male/female ratio of about 2.5/1. More than 90% of patients with oral cavity cancer appear at the age of 45 years and over, and increase steadily until the age of 65 years, then gradually decrease.
Causes of oral cancer
Cigarette: Tobacco is associated with most oral cancers in men and more than half of oral cancers in women. Only about 2-10% of patients with respiratory and upper gastrointestinal cancers do not smoke. All forms of tobacco use increase the risk of oral cancer (cigars, pipes, chewing tobacco, snuff, and reverse smoking). Cigars, pipe smoking have a higher risk of oral cancer than regular cigarettes, pipe smoking also increases the risk of lip cancer.
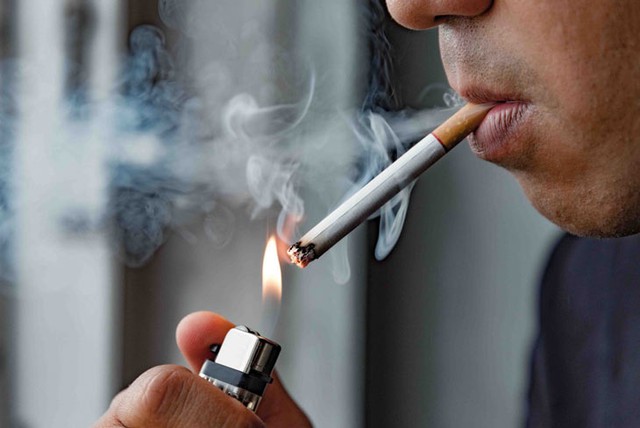

Smoking is the leading cause of oral cancer
Alcohol: Drinking alcohol is also a risk factor for oral cavity cancer. Only less than 3% of patients with respiratory and upper gastrointestinal cancers do not drink alcohol. Alcohol and tobacco work synergistically. A single factor increases the risk of disease by 2-3 times, but when combined, they can increase by 15 times.
HPV: A sexually transmitted virus (usually through oral sex) called human papillomavirus (HPV) can also cause cancer of the oral cavity, especially HPV type 16 infection.
Nutrition: Vitamin A and/or ß-carotene deficiency is a risk factor for oral carcinoma.
Precancerous lesions: Common precancerous lesions in oral cavity cancer are leukoplakia, erythroplasia, and submucosal fibrosis. These lesions are not cancerous but are at risk of becoming cancerous when carcinogenic agents act on them.
– Leukoplakia is a white lesion that does not go away when brushed. Leukoplakia is divided into 4 types: flat, warty, ulcerative and budding. Leukoplakia has an average 6% chance of becoming malignant, 5% for flat, 10% for wart, 15-20% for ulcer, and 55% for flat degeneration.
– Erythema is a red, smooth, velvety, slightly raised lesion with a cancer rate of 33.3%.
– Submucosal fibrosis is a chronic, fibrous scar in the oral cavity, manifested by submucosal fibrous fibers leading to limited mouth and tongue movements.
Signs of oral cancer
– White rice grains, usually appearing in the gums or cheeks and most of the time, there are no symptoms.
– White spots appear on normal mucosal background with rough surface and irregular border.
– Damage to the mucosa caused by dentures or sharp edges and does not heal after 2 weeks.
– Hard submucosal nodule with indistinct border, painless and gradually enlarged. Superficial mucosa is normal.
– Mucosal lesions of unknown cause and do not heal after 2 weeks.
Pain spreading to the ear, bleeding gums can all be symptoms of oral cancer
– Lesions that do not heal after tooth extraction, are red, swollen, and bleed easily when touching the lesion.
An area of the lining of the oral cavity becomes red, painful, and difficult to heal.
– Unexplained pain in the oral cavity, the pain is getting worse.
– Swallowing pain in the ear; speaking difficult; sensation of entanglement in the mouth; spitting up mucus, bloody, and foul smelling
Test method or test
When there are abnormal signs in the mouth, people should check their own health to quickly detect the disease by a number of methods such as:
Lymph node palpation: Palpate the cervical lymph node system, submandibular lymph node, subchin lymph node. Examine both cervical lymph nodes.
Biopsy: The doctor removes a small piece of tissue by surgery, using a needle, or scraping the abnormal area where cancer is suspected. Tissue is examined for cancer cells. This is the best way to know for sure if you have cancer.

Get checked out as soon as you have any unusual symptoms
Dental exam: Your dentist will likely do a full exam, taking X-rays of your teeth and jaw to detect invasive lesions.
The dentist can also remove bad teeth to reduce the risk of tooth decay and infection.
General examination: Detect metastases, cancers associated with or with other diseases, assess the possibility of treatment for each patient.
Ultrasound: Neck ultrasound for lymph nodes, abdominal ultrasound for metastases, and straight lung for metastases. Bone scintigraphy to evaluate bone metastases, diagnose pre-treatment staging, monitor response to treatment, and assess recurrence and metastasis. Renal scintigraphy to assess renal function before and after treatment.
Oral cancer prevention
To prevent cancer in general and oral cancer in particular, it is necessary to prevent and reduce risk factors such as: Periodic specialized examination every 6 months; proper oral hygiene, do not smoke, drink alcohol, stay away from chemical environmental factors, smoke and dust. It is necessary to maintain a healthy diet combined with sports activities to help increase the body’s immunity and protect the body against the risk of diseases.
To promote health and prevent cancer risk, it is necessary to increase the intake of a variety of fruits and vegetables. The vitamins and antioxidants contained in these foods may help reduce the risk of developing oral cancer.
Source: BV 108; Hanoi Oncology Hospital; Vinmec Hospital

By Business and Marketing
at Blogtuan.info – Source: cafebiz.vn – Read the original article here



